Are you at high risk for peripheral artery disease (PAD)?
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease and Why Is It Important to Diagnose?
Pain in the legs and knees of an elderly senior. An old man massages his knees due to severe pain from arthritis and varicose veins[/caption]Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory condition affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when there is a buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the limbs, most commonly the legs. PAD can be a serious health concern, as it increases the risk of complications such as limb amputation and cardiovascular events. In this article, we will explore in detail the signs, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for Peripheral Arterial Disease.
Signs and Symptoms
- Leg Pain: The most common symptom of PAD is leg pain or cramping, especially during physical activity (intermittent claudication). This pain often occurs in the calves, thighs, or buttocks and typically subsides with rest. It is important to note that not everyone with PAD experiences leg pain, especially in the early stages of the disease.
- Numbness or Weakness: Some individuals with PAD may experience numbness, weakness, or a tingling sensation in their legs. This occurs due to inadequate blood supply to the nerves in the affected area.
- Slow Wound Healing: Reduced blood flow can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, leading to delayed wound healing, particularly in the lower extremities. Even minor injuries or sores may take longer to heal or become infected.
- Changes in Skin: PAD may cause the skin on the legs and feet to appear pale, shiny, or discolored. Additionally, the affected area may feel cool to the touch. These changes occur because of reduced blood flow to the skin.
- Poor Nail and Hair Growth: In advanced cases, reduced blood flow can affect nail and hair growth in the affected limb. Nails may become brittle, and hair may become sparse or slow to grow.
Are you asymptomatic?
According to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), approximately 50% of patients with PAD are asymptomatic (Norgren et al., 2007). This finding highlights the importance of early detection and screening for PAD, even in individuals who do not exhibit obvious symptoms. Asymptomatic PAD can still pose serious health risks and increase the likelihood of complications such as limb amputation and cardiovascular events.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing Peripheral Arterial Disease:
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for PAD. The harmful chemicals in tobacco damage the blood vessels, accelerating the development of arterial plaque. Quitting smoking is crucial in managing and preventing PAD.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes have a higher risk of developing PAD due to elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause damage to blood vessels. Proper management of diabetes is essential in reducing the risk and progression of PAD.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure contributes to the development of PAD by putting additional strain on the arterial walls. Controlling blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication can help prevent and manage PAD.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and medications, if necessary, can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of PAD.
- Age and Family History: The risk of PAD increases with age, and individuals with a family history of the disease are more likely to develop it. Regular screenings and awareness of family history are important in early detection and prevention.
Effects on Blood Pressure
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is closely linked to high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. High blood pressure is a common comorbidity with PAD and plays a significant role in exacerbating the condition. The narrowing of peripheral arteries in PAD increases resistance to blood flow, making it harder for blood to pass through. This increased resistance, coupled with the underlying effects of plaque buildup, leads to a rise in blood pressure. The presence of high blood pressure further strains the already compromised peripheral arteries, contributing to the progression of PAD. Moreover, the combination of PAD and high blood pressure significantly heightens the risk of complications, emphasizing the importance of managing blood pressure levels in individuals with PAD. By effectively controlling high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and medications, individuals can reduce the strain on blood vessels, improve circulation, and mitigate the adverse effects of PAD.
Increased Risk for Heart Attack
Peripheral Artery Disease also increases the risk of heart attack or other cardiovascular events. The underlying mechanism is similar to coronary artery disease (CAD), where plaque accumulates in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. When combined with Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), the risk of developing blockages in these arteries further intensifies. The reduced blood flow to the legs and compromised circulation due to PAD can also signify widespread atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of plaque in various arteries throughout the body. This systemic effect heightens the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
Impact on Blood Vessels and Arteries
Peripheral Artery Disease not only affects the peripheral arteries but also has a broader impact on the health of blood vessels throughout the body. The presence of plaque and the resulting narrowing of arteries in the legs is indicative of atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory condition that affects blood vessels. Over time, the inflammatory response triggered by plaque buildup can damage the inner lining of blood vessels, compromising their elasticity and impairing their ability to dilate and constrict as needed. This diminished vascular function can lead to poor circulation, reduced oxygen and nutrient supply to tissues, and increased susceptibility to complications such as non-healing wounds, infections, and tissue damage.
How We Diagnose the Potential of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in Patients of West Coast Podiatry?
It is important if you have leg pain or weakness it is important you visit us right away. Early detection is key to effectively managing the pain and stopping atherosclerosis from progressing
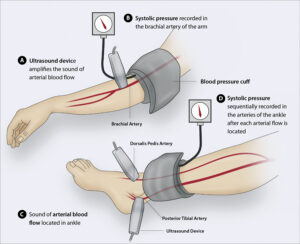
The Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
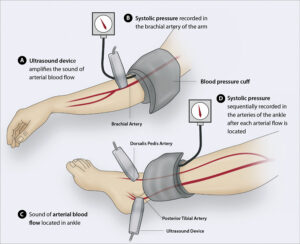
The ankle brachial index (ABI) test is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to assess the presence and severity of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). It measures the ratio of blood pressure at the ankle to the blood pressure in the arm. During the ABI test, blood pressure cuffs are placed on the upper arm and ankles, and blood pressure readings are taken using a Doppler ultrasound device. The systolic pressure (the higher number) is recorded for both the arm and ankle. By comparing the ankle pressure to the arm pressure, the ABI provides an indication of the blood flow in the lower extremities. A normal ABI is typically between 0.9 and 1.3. A lower ABI value suggests reduced blood flow to the legs, indicating the presence of Peripheral Artery Disease. The ABI test is a valuable diagnostic tool as it is non-invasive, simple to perform, and provides quantitative information about the severity of PAD. It helps healthcare professionals identify individuals at risk, determine appropriate treatment plans, and monitor the effectiveness of interventions over time.
Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making positive changes to one’s lifestyle is crucial in managing Peripheral Artery Disease PAD. This includes quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, following a nutritious diet low in saturated fats, and exercising regularly to improve blood flow. Supervised exercise programs, such as walking regimens, are often recommended.
- Medications: Several medications can be prescribed to manage Peripheral Artery Disease. Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, help prevent blood clot formation, reducing the risk of complications. Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins, can slow the progression of arterial plaque. Medications to control blood pressure and blood sugar levels may also be recommended to manage associated conditions.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases where lifestyle changes and medication alone are not sufficient, minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting may be performed. Angioplasty involves widening the narrowed artery using a small balloon, while stenting involves placing a metal mesh tube (stent) to keep the artery open. These procedures help restore blood flow to the affected limb.
- Bypass Surgery: In severe cases of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), bypass surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves using a graft to reroute blood flow around the blocked artery, restoring adequate circulation. Bypass surgery is typically reserved for cases where other treatment options are not feasible or effective.
Conclusion
Peripheral Arterial Disease is a condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the limbs, primarily the legs, due to arterial plaque buildup. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of PAD is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. By understanding the risk factors and implementing lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of developing PAD. At West Coast Podiatry we can review the treatment options ranging from medication to surgical interventions and how you can effectively manage the disease and prevent complications.